17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) were proposed to tackle social, economic, and environmental challenges in the realm of sustainable development, since the 2030 Agenda was unanimously endorsed worldwide in 2015 (United Nations, 2018). The SDG 6—Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all—articulates the augmented concerns not only for sustainable water security issues in the global political program (United Nations, 2018), but also their corresponding impacts across the 2030 Agenda, due to the interlinkages and interdependencies between SDG 6 and other SDGs (Taka et al., 2021). Therefore, how to achieve sustainable water security in accordance with Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 6 targets has become a new measure of curbing water risk.
In this research, we developed a composite SDG 6 index (SDG6I) as a tool for empowering adequate policy measures towards the delivery of sustainable water security throughout the world. The seven SDG indicators covering five outcome-based targets were selected to systematically portray diverse water challenges (drinking water, sanitation and hygiene, wastewater treatment, water productivity, water stress, water resources management, and transboundary cooperation) for integrated water risk assessment. A quantitative spatial analysis was conducted to explore the global implementation baseline of the SDG 6 indicators and subsequently the SDG6I by country (See Figure 1). Our study is the first one to systematically assess water risk by a composite index built upon the SDG 6 targets and their indicators.
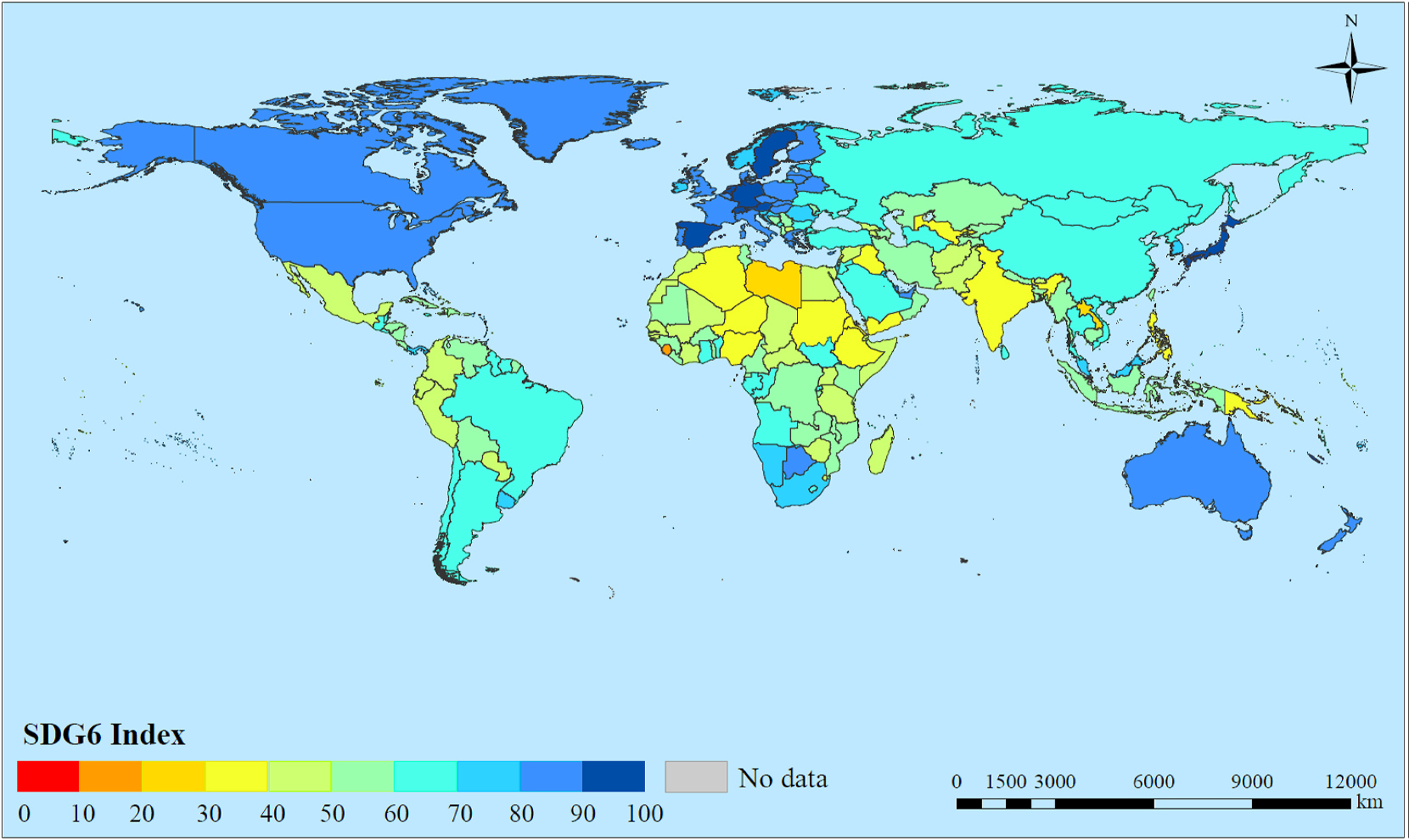
Figure 1. Global baseline of SDG 6 index by country and territory
Our results showed that most countries are on track to achieve universal water accessibility by 2030, yet African countries in general need to strengthen the implementation capacity of service coverage. Second, only countries in Australia and New Zealand as well as Europe and Northern America are on track to achieve the targets of water quality and water availability. Additionally, the notable variation in the SDG 6 indicators and SDG6I was also clearly portrayed (See Figure 2 ). In spite of I642 (water stress) being exceptional, there were gradually decreasing trends from the very high Human Development group to the low Human Development group regarding the implementation level of the SDG6I and other six SDG 6 indicators. This reveals that the degree of a country’s socioeconomic development largely preconditions its progress on SDG 6 and the challenges it confronts in the SDG 6 dimensions.
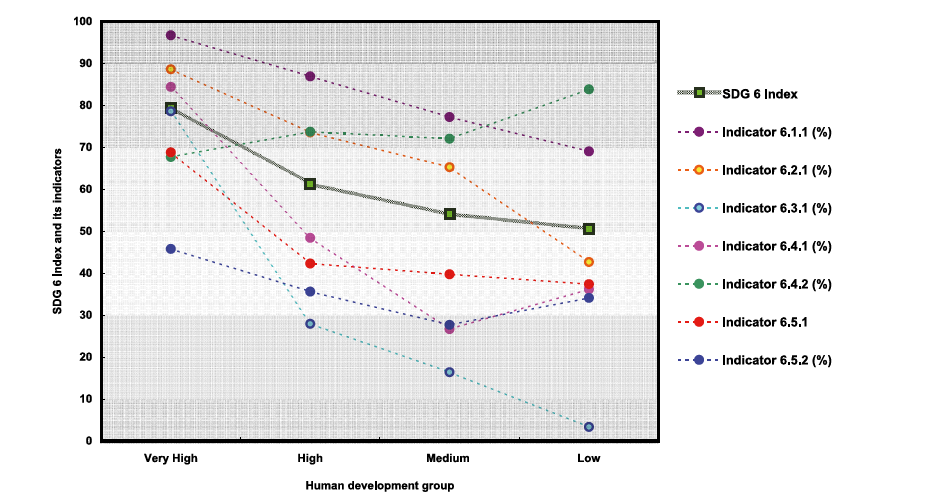
Figure 2. Global baseline of SDG 6 index and its indicators by Human Development Index (HDI)
In accordance with the baseline profiles, the policy implications of the SDG6I and its indicators were subsequently investigated. It led to three adequate macro-scale policy measures to curb water risk, i.e., promoting socioeconomic development, improving policy effectiveness, and fostering multi-level governance and collaboration. Due to many deep interlinkages and interdependencies, these measures need to be designed and implemented through nexus thinking to deliver sustainable water security, particularly in the context of the adverse impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on SDG 6 progress (See Figure 3).
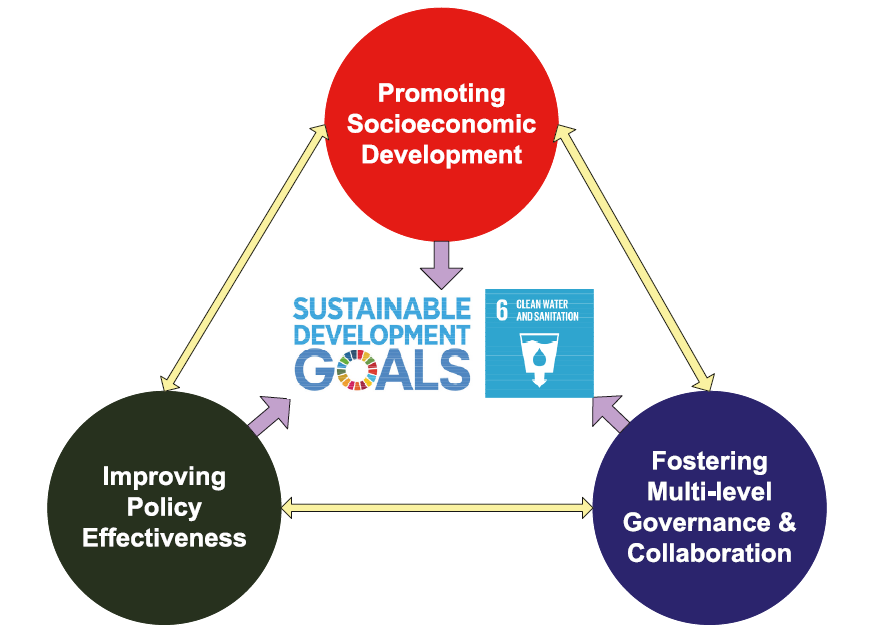
Figure 3. Adequate policy measures for curbing water risk through nexus thinking.
Finally, the innovative contributions that this study made shed some light on the applicability of the SDG Index construction, with the key points below:
- The index construction requires the indicator framework to follow the “STAR” protocol (Straightforwardness, Transparency, Availability, and Readiness).
- The indicator framework, owing to its dynamic nature, needs to be examined within a specific time period for refining the index construction.
- Mapping synergies and trade-offs among different SDGs across the 2030 Agenda can be reinforced with the standardized procedures of the index construction.
Read the full article: CAI, Jialiang; ZHAO, Dandan; VARIS, Olli. Match words with deeds: Curbing water risk with the Sustainable Development Goal 6 index. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 318:128509. (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652621027190 )

Dandan Zhao works as a postdoctoral researcher in WDRG. Her research interests include water footprint, virtual water trade, ecological economics, environmental input-output analysis and water-energy-food nexus.

